Oxidation-Resistant Amorphous Zinc Tin Nitride Films with Tunable Optical and Electrical Properties
- Journal
- Chemistry of Materials
- Page
- 6802-6808
- Year
- 2022
- Link
- https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.2c00940 604회 연결
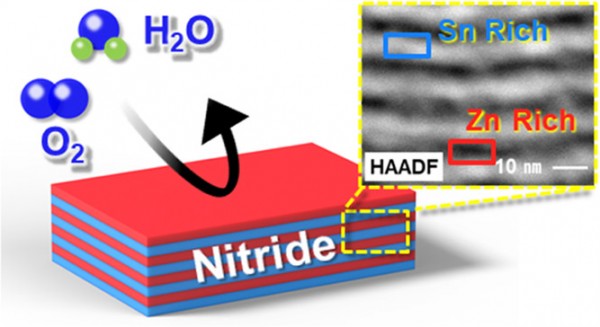
Zinc tin nitride (ZTN) compounds exhibit excellent optical and defect-tolerance properties desirable for optoelectronic applications. However, the synthesis of high-phase-purity ZTN is limited by oxidation. We report the synthesis of amorphous ZTN films with excellent oxidation resistance for a wide range of compositions (from pure Zn3N2 to ZTN with Sn/(Sn + Zn) up to 66.9%). We employ modified pulsed plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition with alternating pulses of zinc and tin precursors. We observe a correlation between oxidation resistance and pulse duration of the Zn precursor. Furthermore, extensive structural, chemical, electrical, and optical characterizations are discussed for amorphous ZTN with varying Sn/Zn. Electron microscopy reveals a mixture of nanoscale domains with Zn-rich and Sn-rich phases in the synthesized films. Interestingly, the trends of the electrical and optical properties vs the Sn content of amorphous ZTN are similar to reported crystalline ZTN. Notably, amorphous ZTN of Sn/(Zn + Sn) ∼ 0.3 exhibited a carrier concentration of 5.3 × 1013 cm–3, the lowest among those reported for ZTN of any composition, making it very promising for photovoltaic applications. Our study presents a new class of compounds with materials properties that are unaccessible by the conventional crystalline nitrides, which will be useful for future optoelectronic applications.